BigO Notation
Definition
Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument approaches infinity.
Purpose
It is commonly used in computer science to analyze the performance and efficiency of algorithms.
Representations
Big O notation is expressed as O(f(n)), where “f(n)” represents the growth rate of an algorithm in terms of the input size (n).
Key Terms
O(f(n)): Upper bound. Describes the worst-case scenario. Ω(f(n)): Lower bound. Describes the best-case scenario. Θ(f(n)): Tight bound. Describes both the upper and lower bounds, indicating a precise growth rate.
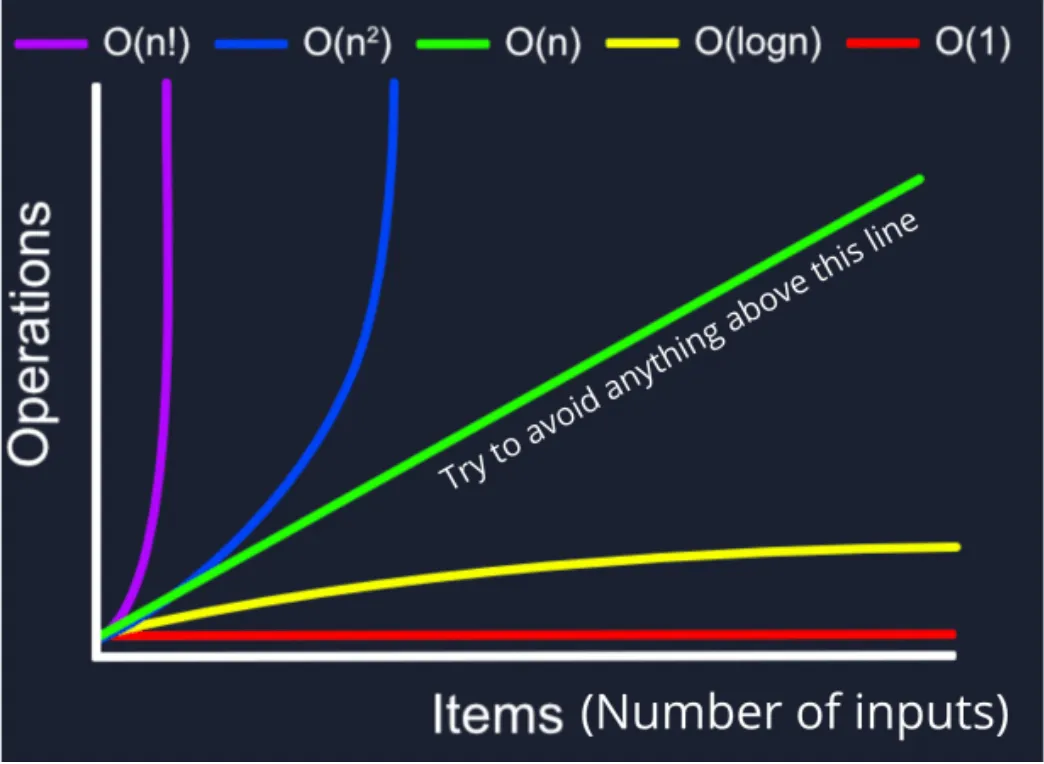
Common Notations:
O(1): Constant time complexity. The algorithm’s performance is constant, regardless of input size. O(log n): Logarithmic time complexity. Common in algorithms that divide the problem in half at each step (e.g., binary search). O(n): Linear time complexity. The running time grows linearly with the input size. O(n log n): Linearithmic time complexity. Common in efficient sorting algorithms (e.g., merge sort, heap sort). O(n^2): Quadratic time complexity. Common in algorithms with nested iterations. O(2^n): Exponential time complexity. Often found in algorithms with recursive solutions that solve a problem of size “n” by recursively solving two smaller problems.
Rules:
When analyzing an algorithm, focus on the dominant term with the highest impact on the overall growth rate. Constants and lower-order terms are usually dropped in Big O notation.
Example:
If an algorithm has a time complexity of O(2n^2 + 3n + 1), it is simplified to O(n^2) since the quadratic term dominates.
Importance:
Big O notation provides a high-level understanding of how the runtime or space requirements of an algorithm scale with input size.
Considerations:
Big O notation represents an upper bound, and actual performance may be better (lower) than the stated complexity.
Practical Use:
Engineers and developers use Big O notation to make informed decisions about algorithm selection, especially when dealing with large datasets.